ABC Transporter B4: Role In Drug Resistance And Therapeutic Implications
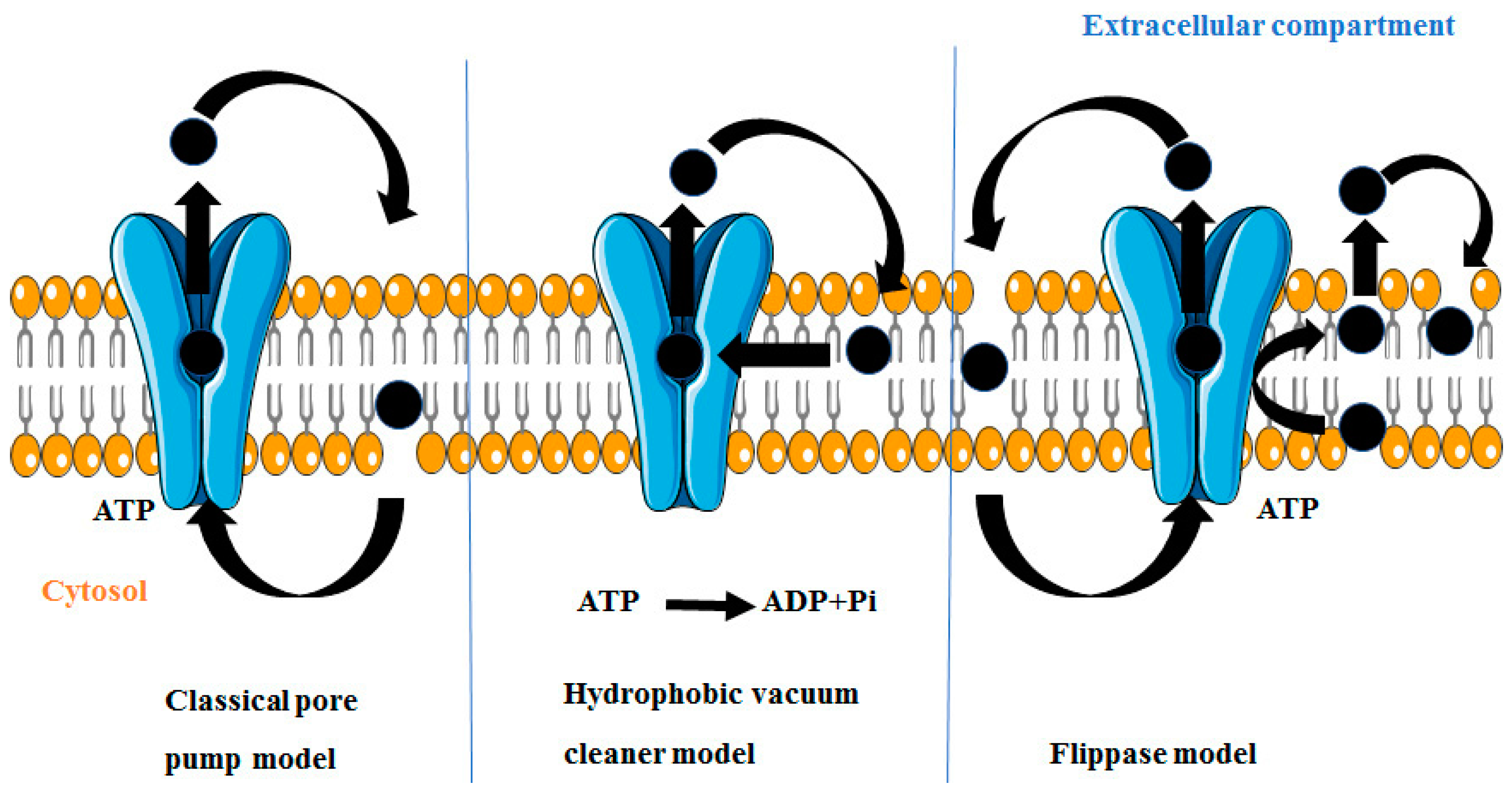
P Gp And Bcrp Efflux Transporters - Transport Informations Lane - Source www.peregene.com
Editor's Notes: "ABC Transporter B4: Role In Drug Resistance And Therapeutic Implications" have published on [publish date]. Study shows that it helps to understand "ABC Transporter B4: Role In Drug Resistance And Therapeutic Implications" and this study was conducted by an experienced team.
To help target audience understand "ABC Transporter B4: Role In Drug Resistance And Therapeutic Implications", we have done some analysis, digging information, and put together this guide.
Key differences or Key takeways
| Key | ABC Transporter B4 |
|---|---|
| Role | Drug Resistance, Therapeutic Implications |
Transition to main article topics
FAQs
This FAQ section provides comprehensive answers to frequently asked questions regarding the role of ABC Transporter B4 in drug resistance and its therapeutic implications.
Question 1: What is ABC Transporter B4?
ABC Transporter B4 (ABCB4) is a member of the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter superfamily, responsible for transporting various molecules across cellular membranes. It plays a crucial role in drug resistance, as it can efflux drugs out of cells, reducing their intracellular concentration and effectiveness.

ABC transporter – Ritu's Biology Hub - Source www.ritubiology.com
Question 2: How does ABCB4 contribute to drug resistance?
ABCB4 transports drugs out of cells by utilizing ATP hydrolysis. This efflux activity effectively reduces the intracellular drug concentration, making the cells less susceptible to the drug's effects. The overexpression of ABCB4 can significantly increase drug resistance, rendering treatment less effective.
Question 3: What therapeutic strategies target ABCB4?
Overcoming ABCB4-mediated drug resistance is a major focus in developing new therapeutic strategies. One approach involves the use of ABCB4 inhibitors, which block the transporter's function and allow drugs to accumulate within cells. Additionally, targeting the expression or activity of ABCB4 can enhance the efficacy of chemotherapy drugs.
Question 4: What are the clinical implications of ABCB4?
ABCB4 overexpression has been associated with poor prognosis and reduced treatment response in various cancers. It contributes to multidrug resistance, where tumors become resistant to multiple drugs, making treatment more challenging. Understanding the role of ABCB4 in drug resistance is crucial for developing personalized treatment strategies and improving therapeutic outcomes.
Question 5: How can we prevent or overcome ABCB4-mediated drug resistance?
Overcoming ABCB4-mediated drug resistance requires a multidisciplinary approach. Identifying patients with ABCB4 overexpression can guide treatment decisions. Additionally, combination therapies that target ABCB4 and other resistance mechanisms can improve treatment efficacy. Further research is needed to develop novel strategies to circumvent ABCB4-mediated drug resistance.
Question 6: What are the future directions of research on ABCB4?
Continued research on ABCB4 is essential to fully understand its role in drug resistance and develop effective therapeutic strategies. Investigations into the molecular mechanisms of ABCB4 regulation and efflux activity will provide valuable insights. Furthermore, identifying novel ABCB4 inhibitors and exploring their potential in combination therapies hold promise for improving cancer treatment outcomes.
In conclusion, ABCB4 plays a significant role in drug resistance, impacting the efficacy of chemotherapy and affecting patient outcomes. Understanding the mechanisms of ABCB4-mediated drug resistance is crucial for developing tailored therapeutic strategies and improving treatment success.
Next: Explore the challenges and opportunities in targeting ABCB4 for cancer therapy.
Tips by ABC Transporter B4: Role In Drug Resistance And Therapeutic Implications
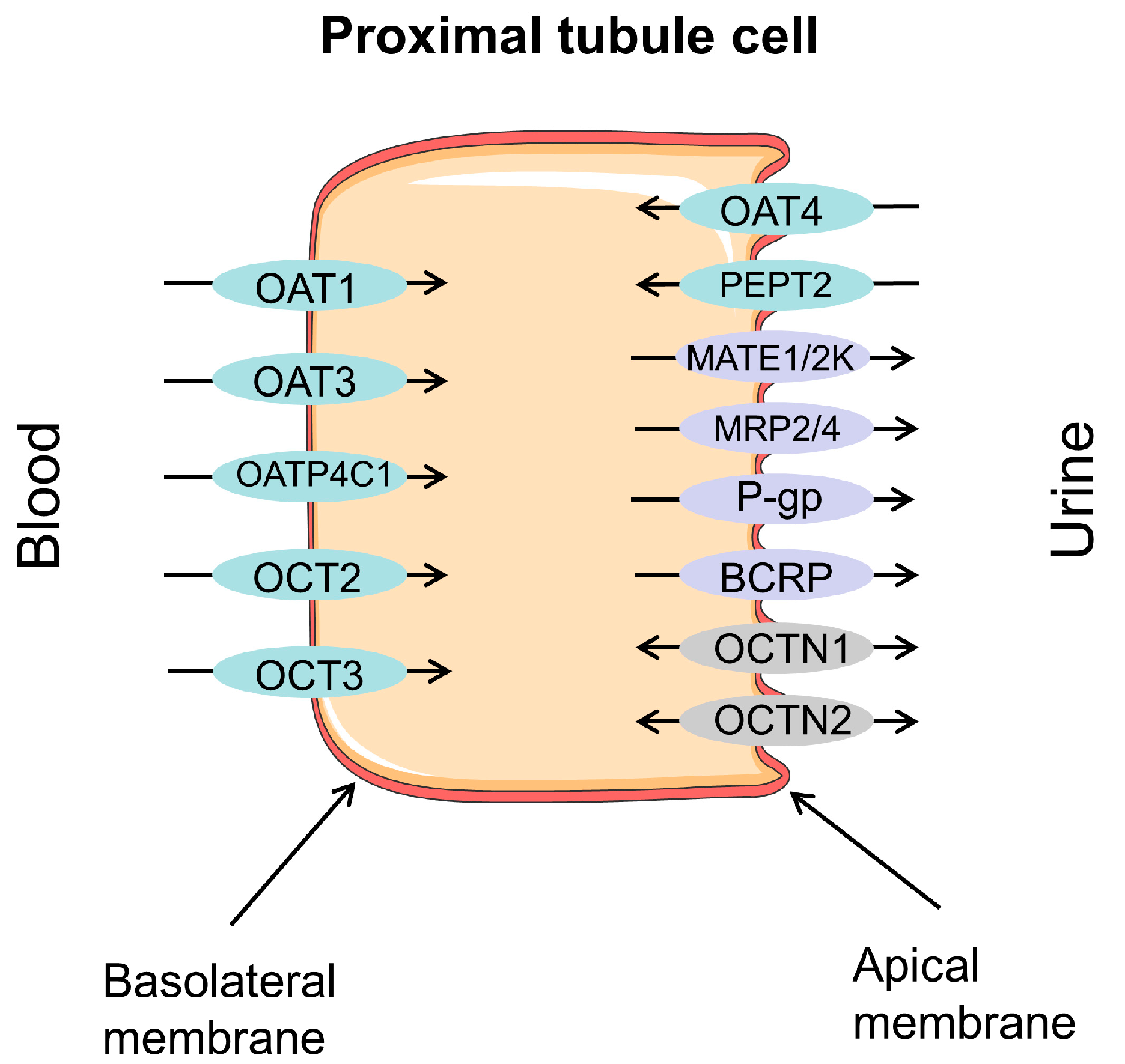
Hepatocyte Transporter 1 Oct - Source ar.inspiredpencil.com
Tip 1: Understand the role of ABCB4 in drug resistance. ABCB4 is a member of the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter family, which are responsible for the efflux of various compounds from cells. ABCB4 has been shown to be involved in the efflux of a wide range of drugs, including chemotherapeutic agents, antibiotics, and antiviral drugs. As a result, ABCB4 can contribute to drug resistance in cancer cells and other types of cells.
Tip 2: Identify inhibitors of ABCB4. The development of inhibitors of ABCB4 could be a promising strategy to overcome drug resistance. Several compounds have been identified that can inhibit ABCB4 activity, including verapamil, cyclosporine A, and PSC833. These inhibitors could be used to increase the efficacy of chemotherapeutic agents and other drugs that are substrates of ABCB4.
Tip 3: Use ABCB4 expression as a biomarker for drug resistance. The expression of ABCB4 can be used as a biomarker for drug resistance. Cells that express high levels of ABCB4 are more likely to be resistant to drugs that are substrates of ABCB4. This information can be used to guide treatment decisions and to identify patients who are at high risk for developing drug resistance.
ABC Transporter B4: Role In Drug Resistance And Therapeutic Implications
The ATP-binding cassette transporter B4 (ABCB4) plays a pivotal role in various physiological processes, notably in drug resistance and response to therapy. Here are six essential aspects of ABCB4 in this context:
- Drug Efflux: ABCB4 actively transports a wide range of drugs out of cells, reducing their intracellular accumulation and cytotoxic effects.
- Multidrug Resistance: ABCB4 overexpression is implicated in multidrug resistance, where cancer cells exhibit decreased susceptibility to multiple structurally unrelated chemotherapeutic agents.
- Tumor Progression: ABCB4 expression has been linked to tumor growth, metastasis, and angiogenesis, highlighting its role in cancer progression.
- Prognostic Marker: High ABCB4 expression in tumors often correlates with poor prognosis and reduced patient survival, indicating its clinical significance.
- Therapeutic Target: Targeting ABCB4 has emerged as a potential therapeutic strategy to overcome drug resistance and enhance the efficacy of chemotherapy.
- Natural Products: Certain natural products have been identified that inhibit ABCB4 function, suggesting potential for developing new chemosensitizing agents.
Understanding the multiple facets of ABCB4 in drug resistance and therapeutic implications is crucial for advancing cancer treatment strategies. Inhibition of ABCB4 has the potential to restore drug sensitivity, improve therapeutic outcomes, and potentially prolong survival in cancer patients.
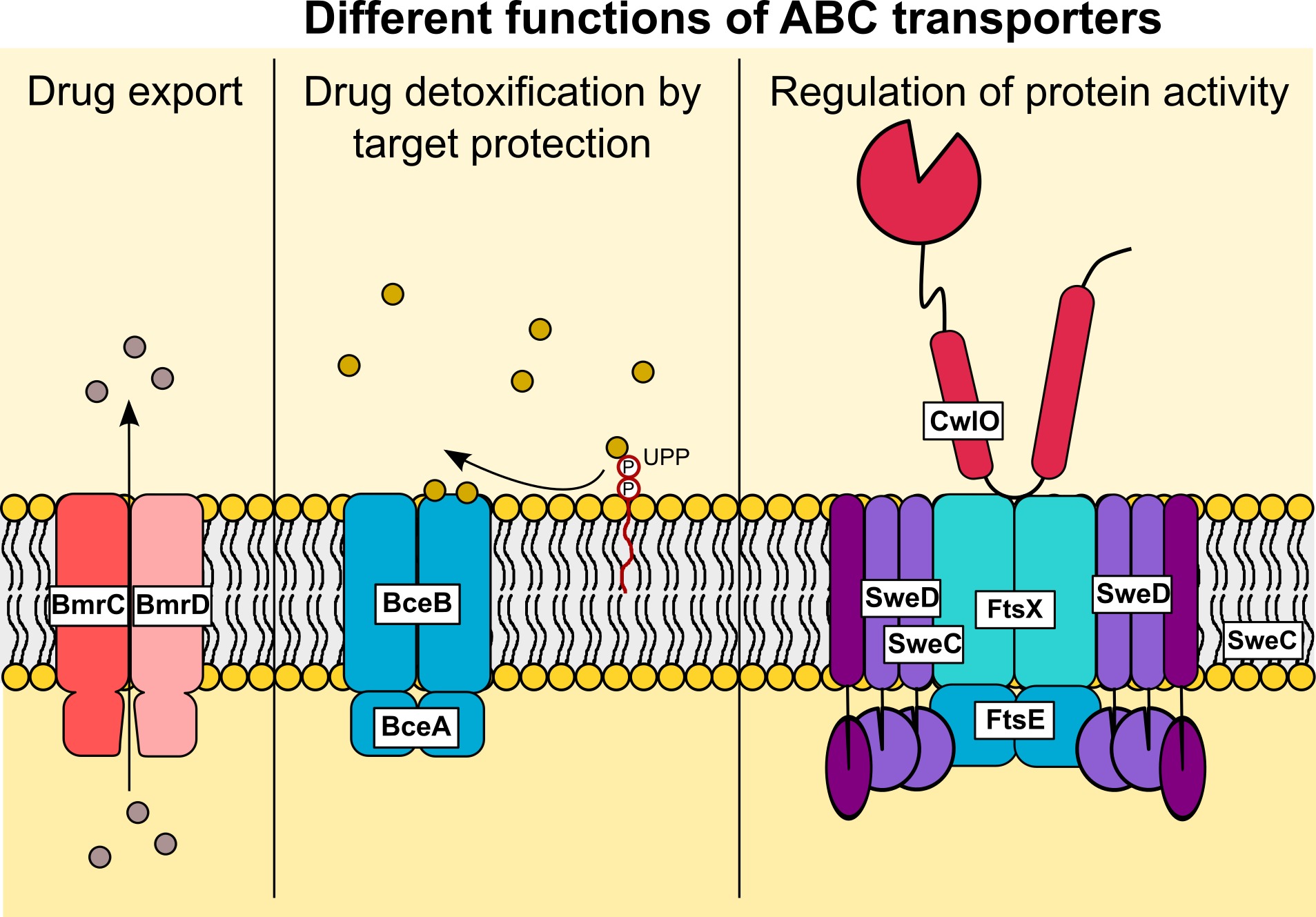
reqopwired - Blog - Source reqopwired.weebly.com

Structure And Function Of Hepatobiliary ATP Binding, 42% OFF - Source www.oceanproperty.co.th
ABC Transporter B4: Role In Drug Resistance And Therapeutic Implications
ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters are a large family of membrane proteins that play an important role in the transport of a wide variety of molecules across cell membranes. One of the most well-studied ABC transporters is ABCB4, which is responsible for the efflux of drugs from cells. ABCB4 is overexpressed in many cancer cells, and this overexpression is associated with drug resistance.

Journal of Molecular Cell Biology | Oxford Academic - Source academic.oup.com
The overexpression of ABCB4 in cancer cells is a major obstacle to the effective treatment of cancer. Several strategies have been developed to overcome ABCB4-mediated drug resistance, including the use of inhibitors of ABCB4 and the use of drugs that are not substrates for ABCB4.
The inhibition of ABCB4 is a promising strategy to overcome drug resistance. Several ABCB4 inhibitors have been developed, and some of these inhibitors have shown promising results in clinical trials. However, the development of ABCB4 inhibitors has been hampered by the fact that ABCB4 is also expressed in normal cells. This means that ABCB4 inhibitors can have toxic side effects.
The use of drugs that are not substrates for ABCB4 is another strategy to overcome ABCB4-mediated drug resistance. Several drugs that are not substrates for ABCB4 have been identified, and some of these drugs have shown promising results in clinical trials. However, the development of drugs that are not substrates for ABCB4 has been hampered by the fact that these drugs may have other side effects.
The overexpression of ABCB4 in cancer cells is a major obstacle to the effective treatment of cancer. Several strategies have been developed to overcome ABCB4-mediated drug resistance, but these strategies have had limited success. Further research is needed to develop new strategies to overcome ABCB4-mediated drug resistance.
Conclusion
The overexpression of ABCB4 in cancer cells is a major obstacle to the effective treatment of cancer. Several strategies have been developed to overcome ABCB4-mediated drug resistance, but these strategies have had limited success. Further research is needed to develop new strategies to overcome ABCB4-mediated drug resistance.
ABC transporter B4 (ABCB4) is a membrane protein that plays an important role in the transport of drugs and other molecules across cell membranes. ABCB4 is overexpressed in many cancer cells, and this overexpression is associated with drug resistance. The development of new strategies to overcome ABCB4-mediated drug resistance is an important area of research.



